2-简单工厂/工厂方法(常用)
简单工厂(Simple Factory)
Intent
在创建一个对象时不向客户暴露内部细节,并提供一个创建对象的通用接口。
Class Diagram
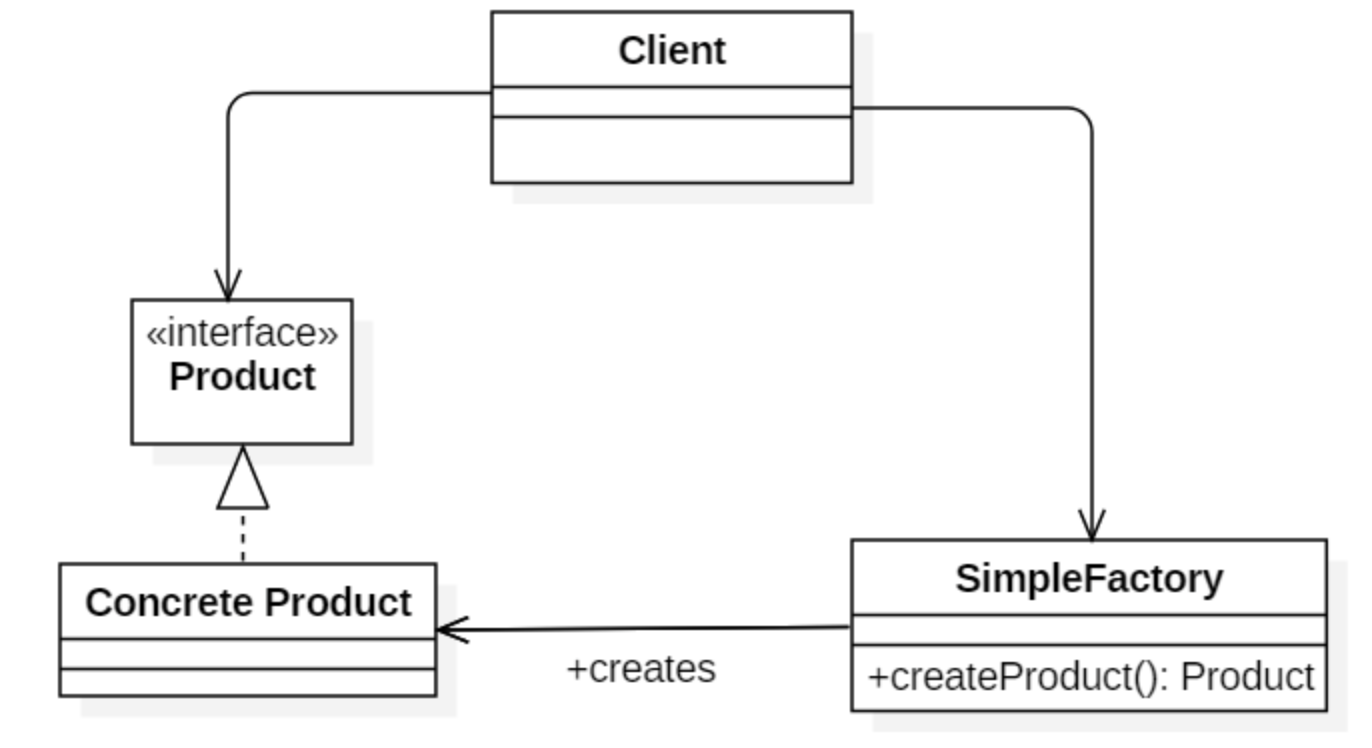
简单工厂把实例化的操作单独放到一个类中,这个类就成为简单工厂类,让简单工厂类来决定应该用哪个具体子类来实例化。
这样做能把客户类和具体子类的实现解耦,客户类不再需要知道有哪些子类以及应当实例化哪个子类。客户类往往有多个,如果不使用简单工厂,那么所有的客户类都要知道所有子类的细节。而且一旦子类发生改变,例如增加子类,那么所有的客户类都要进行修改。
Implementation
public interface Product {
}public class ConcreteProduct implements Product {
}public class ConcreteProduct1 implements Product {
}public class ConcreteProduct2 implements Product {
}以下的 Client 类包含了实例化的代码,这是一种错误的实现。如果在客户类中存在这种实例化代码,就需要考虑将代码放到简单工厂中。
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int type = 1;
Product product;
if (type == 1) {
product = new ConcreteProduct1();
} else if (type == 2) {
product = new ConcreteProduct2();
} else {
product = new ConcreteProduct();
}
// do something with the product
}
}以下的 SimpleFactory 是简单工厂实现,它被所有需要进行实例化的客户类调用。
public class SimpleFactory {
public Product createProduct(int type) {
if (type == 1) {
return new ConcreteProduct1();
} else if (type == 2) {
return new ConcreteProduct2();
}
return new ConcreteProduct();
}
}public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleFactory simpleFactory = new SimpleFactory();
Product product = simpleFactory.createProduct(1);
// do something with the product
}
}工厂方法(Factory Method)
Intent

定义了一个创建对象的接口,但由子类决定要实例化哪个类。工厂方法把实例化操作推迟到子类。
理解:抽象工厂实现公用的逻辑,由子类实现具体的逻辑
例如:外显号码策略工厂、中继获取策略工厂
Class Diagram
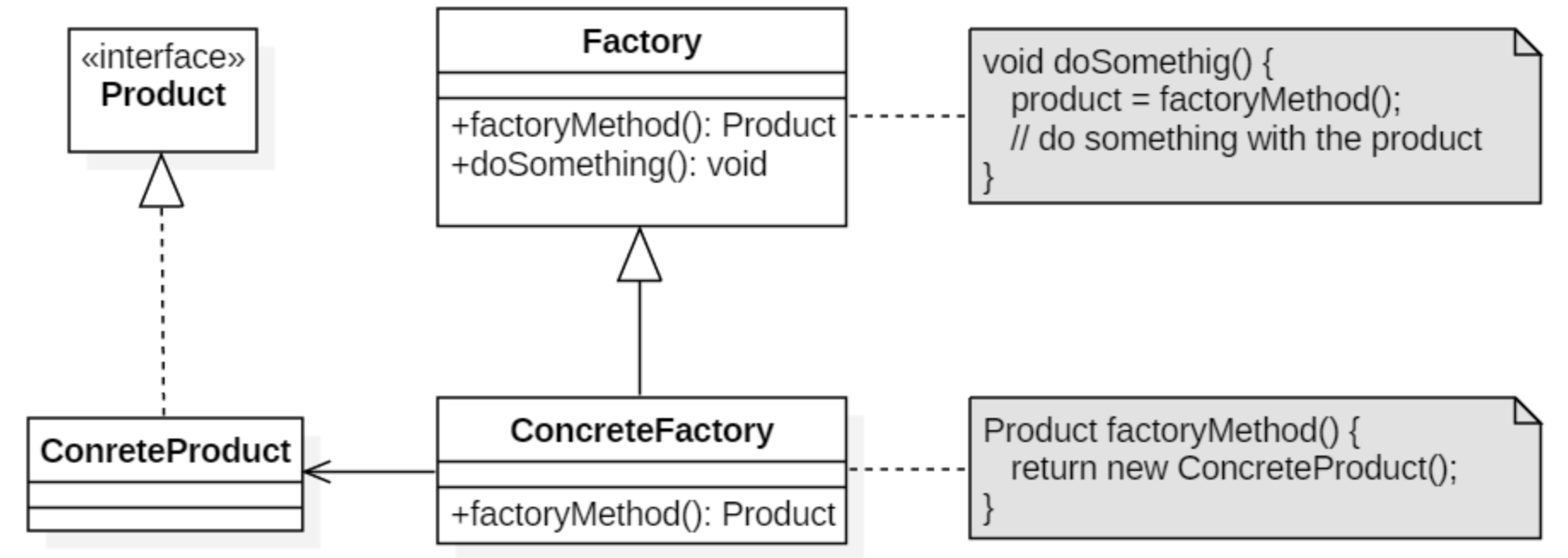
在简单工厂中,创建对象的是另一个类,而在工厂方法中,是由子类来创建对象。
下图中,Factory 有一个 doSomething() 方法,这个方法需要用到一个产品对象,这个产品对象由 factoryMethod() 方法创建。该方法是抽象的,需要由子类去实现。
Implementation
public abstract class Factory {
abstract public Product factoryMethod();
public void doSomething() {
Product product = factoryMethod();
// do something with the product
}
}public class ConcreteFactory extends Factory {
public Product factoryMethod() {
return new ConcreteProduct();
}
}public class ConcreteFactory1 extends Factory {
public Product factoryMethod() {
return new ConcreteProduct1();
}
}public class ConcreteFactory2 extends Factory {
public Product factoryMethod() {
return new ConcreteProduct2();
}
}Business Scenario
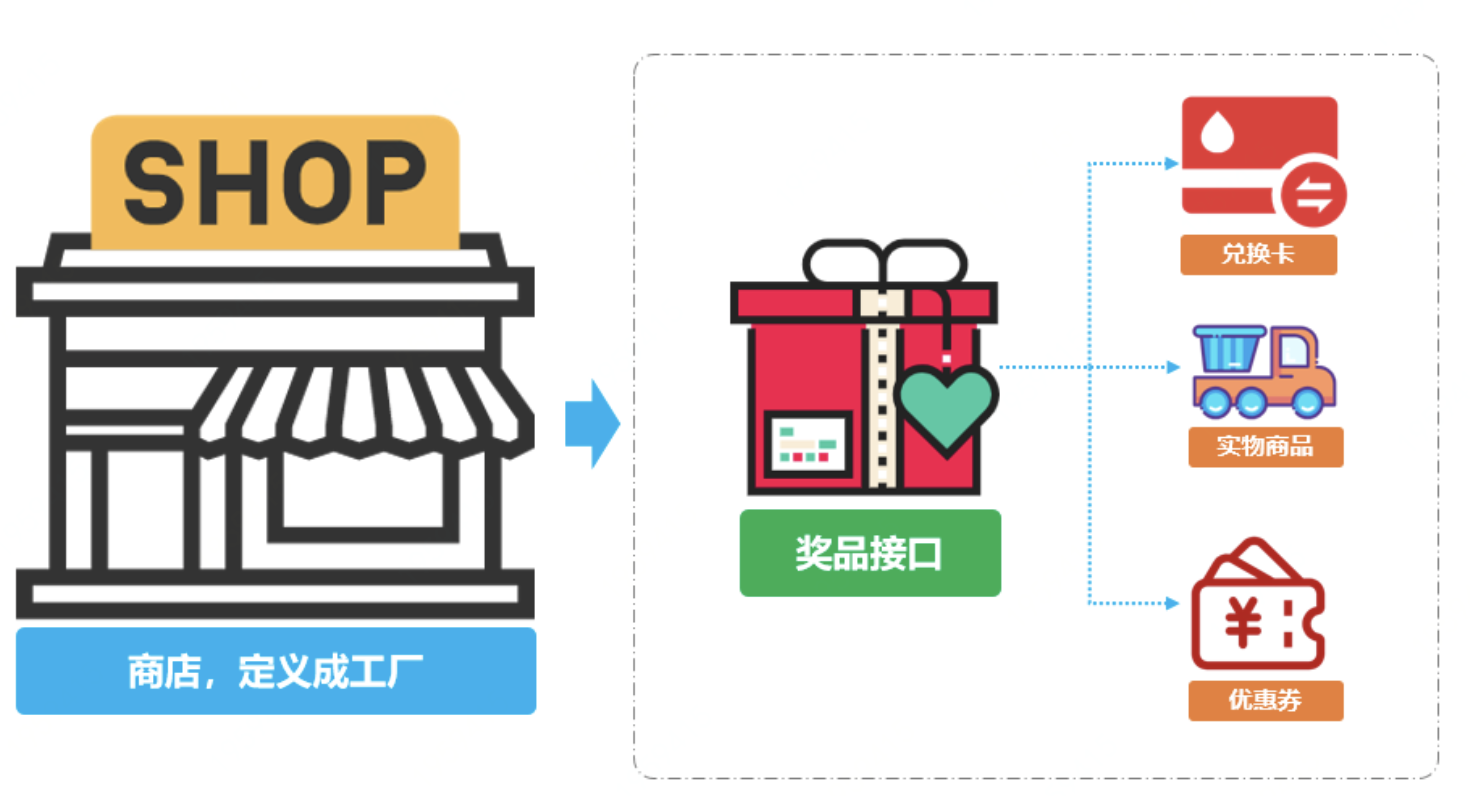
模拟互联网中在营销场景下的业务。由于营销场景的复杂、多变、临时的特性,它所需要的设计需要更加深入,否则会经常面临各种紧急CRUD操作,从而让代码结构混乱不堪,难以维护。在营销场景中经常会有某个用户做了一些操作;打卡、分享、留言、邀请注册等等,进行返利积分,最后通过积分在兑换商品,从而促活和拉新。
那么在这里我们模拟积分兑换中的发放多种类型商品,假如现在我们有如下三种类型的商品接口;
序号 | 类型 | 接口 |
|---|---|---|
1 | 优惠券 | CouponResult sendCoupon(String uId, String couponNumber, String uuid) |
2 | 实物商品 | Boolean deliverGoods(DeliverReq req) |
3 | 第三⽅方爱奇艺 兑换卡 | void grantToken(String bindMobileNumber, String cardId) |
接口返回类型不同,有对象类型、布尔类型、还有一个空类型。
入参不同,发放优惠券需要仿重、兑换卡需要卡D、实物商品需要发货位置(对象中含有)。
可能会随着后续的业务的发展,会新增其他种商品类型。因为你所有的开发需求都是随着业务对市场的拓展而带来的。
使用工厂方法实现:
奖品接口:
/**
* 奖品接口
*/
public interface ICommodity {
void sendCommodity(String uId, String commodityId, String bizId, Map<String, String> extMap) throws Exception;
}奖品实现方式:
/**
* 会员卡模拟service
*/
public class CardCommodityService implements ICommodity {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CardCommodityService.class);
// 模拟注入
private IQiYiCardService iQiYiCardService = new IQiYiCardService();
@Override
public void sendCommodity(String uId, String commodityId, String bizId, Map<String, String> extMap) throws Exception {
String mobile = queryUserMobile(uId);
iQiYiCardService.grantToken(mobile, bizId);
logger.info("请求参数[爱奇艺兑换卡] => uId:{} commodityId:{} bizId:{} extMap:{}", uId, commodityId, bizId, JSON.toJSON(extMap));
logger.info("测试结果[爱奇艺兑换卡]:success");
}
private String queryUserMobile(String uId) {
return "15200101232";
}
}/**
* 优惠券模拟service
*/
public class CouponCommodityService implements ICommodity {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CouponCommodityService.class);
private CouponService couponService = new CouponService();
@Override
public void sendCommodity(String uId, String commodityId, String bizId, Map<String, String> extMap) throws Exception {
CouponResult couponResult = couponService.sendCoupon(uId, commodityId, bizId);
logger.info("请求参数[优惠券] => uId:{} commodityId:{} bizId:{} extMap:{}", uId, commodityId, bizId, JSON.toJSON(extMap));
logger.info("测试结果[优惠券]:{}", JSON.toJSON(couponResult));
if (!"0000".equals(couponResult.getCode())) {
throw new RuntimeException(couponResult.getInfo());
}
}
}/**
* 实物商品发放service
*/
public class GoodsCommodityService implements ICommodity {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GoodsCommodityService.class);
private GoodsService goodsService = new GoodsService();
@Override
public void sendCommodity(String uId, String commodityId, String bizId, Map<String, String> extMap) throws Exception {
DeliverReq deliverReq = new DeliverReq();
deliverReq.setUserName(queryUserName(uId));
deliverReq.setUserPhone(queryUserPhoneNumber(uId));
deliverReq.setSku(commodityId);
deliverReq.setOrderId(bizId);
deliverReq.setConsigneeUserName(extMap.get("consigneeUserName"));
deliverReq.setConsigneeUserPhone(extMap.get("consigneeUserPhone"));
deliverReq.setConsigneeUserAddress(extMap.get("consigneeUserAddress"));
Boolean isSuccess = goodsService.deliverGoods(deliverReq);
logger.info("请求参数[优惠券] => uId:{} commodityId:{} bizId:{} extMap:{}", uId, commodityId, bizId, JSON.toJSON(extMap));
logger.info("测试结果[优惠券]:{}", isSuccess);
if (!isSuccess) {
throw new RuntimeException("实物商品发放失败");
}
}
private String queryUserName(String uId) {
return "花花";
}
private String queryUserPhoneNumber(String uId) {
return "15200101232";
}
}商品发放工厂(根据类型发放商品):
/**
* 商品工厂
*/
public class StoreFactory {
public ICommodity getCommodityService(Integer commodityType) {
if (null == commodityType) {
return null;
}
if (1 == commodityType) {
return new CouponCommodityService();
}
if (2 == commodityType) {
return new GoodsCommodityService();
}
if (3 == commodityType) {
return new CardCommodityService();
}
throw new RuntimeException("不存在的商品服务类型");
}
}测试类
public class ApiTest {
@Test
public void test_commodity() throws Exception {
StoreFactory storeFactory = new StoreFactory();
// 1. 优惠券
ICommodity commodityService_1 = storeFactory.getCommodityService(1);
commodityService_1.sendCommodity("111", "222", "333", null);
// 2. 实物商品
ICommodity commodityService_2 = storeFactory.getCommodityService(2);
Map<String,String> extMap = new HashMap<String,String>();
extMap.put("consigneeUserName", "小z");
extMap.put("consigneeUserPhone", "11111111111");
extMap.put("consigneeUserAddress", "北京市朝阳区....");
commodityService_2.sendCommodity("111","222","333",new HashMap<String, String>() {{
put("consigneeUserName", "小z");
put("consigneeUserPhone", "11111111111");
put("consigneeUserAddress", "北京市朝阳区....");
}});
// 3. 第三方兑换卡(爱奇艺)
ICommodity commodityService_3 = storeFactory.getCommodityService(3);
commodityService_3.sendCommodity("111","222",null,null);
}
}Summary
工厂方法实现简单,隐藏了产品创建的实现,更加易于扩展
